
# Pass the above given matrix as an argument to the random. Print("The given matrix is:\n", gvn_matx) # Print the above given matrix (multi-dimensional array) # number of rows and columns using the reshape() function I need this for an experiment I am designing, where searching for this small scrambled circle will act as a low-level perceptual part of a task. # to get a list containing elements in given range and reshape it to given I'm completely stuck on this problem - I need to randomly permute the pixels within a circle on a 2D image. Print the above-given matrix after permuting randomly.Pass the above given matrix as an argument to the random.permutation() function to randomly permute the elements of the above matrix.Print the above-given matrix (multi-dimensional array).
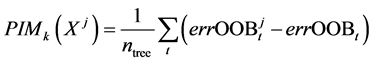

Pass the lower and upper limit range as arguments to the arange() function to get a list containing elements in the given range and reshape it to the given number of rows and columns using the reshape() function.NP.random.permutation: When used with a multi-dimensional array, the function just permutes the items along the first axis. Print("The above given list after permuting:", rslt) # Print the above given list after permuting # to randomly permute the elements of the above list # Pass the above given list as an argument to the random.permutation() function # to get a list containing elements in given range(0 to 7 here) # Pass the lower and upper limit range as arguments to the arange() function Print the above-given list after permuting randomly.īelow is the implementation: # Import numpy module using the import keyword.Pass the above given list as an argument to the random.permutation() function to randomly permute the elements of the above list.Pass the lower and upper limit range as arguments to the arange() function to get a list containing elements in the given range(0 to 7 here).Import numpy module using the import keyword.NumPy random.permutation() Function in Python Permutation is a mathematical name for an arrangement.

Your job is to write a program that produces random permutations of the numbers 1 to 10. Python NumPy random.random_sample() Function Professor Snoop wants a program that will randomly generate 10 unique random numbers.If x is an integer, permute np.arange(x) at random.Ī permuted sequence or array range is returned The array or list to be shuffled is specified by this. If x is a multidimensional array, only the first axis is shuffled. Numpy random permutation: The permutation() function of the NumPy random module can randomly permute a sequence or return a permuted range.
Randomly permute python generator#
This module includes some basic random data generating methods, as well as permutation and distribution functions and random generator functions. This module includes the functions for generating random numbers. # (0, 1, 2, 4, 3) Fix the random number seedīy giving an arbitrary integer to the random module's function seed(), the random number seed can be fixed and the random number generator can be initialized.Īfter initialization with the same seed, it is always reordered in the same way.NP random permutation: The random module is part of the NumPy library. sample(s, len(s)))įor tuples, use tuple(), which creates a tuple from a list. To concatenate them into a single string again, use the join() method. In the case of a string, it will be a list of characters one by one. If you want to shuffle a string or tuple, use random.sample(), which creates a new object.Įven when a string or tuple is specified as an argument, random.sample() returns a list, so it is necessary to process it back to a string or tuple. # (0, 1, 2, 3, 4) # random.shuffle(t) # TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment TypeError s = 'abcde' # random.shuffle(s) # TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment Strings and tuples are immutable, so if you use random.shuffle() to change the original object, you will get the following error. The total number of elements in the list is obtained by len(). If the number of elements to be selected by sample() is the total number of elements in the list, we get a new list with all elements randomly sorted.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
